Downloads
Tutorial
Sample Code
Screenshots
Getting Started
FAQ
Support

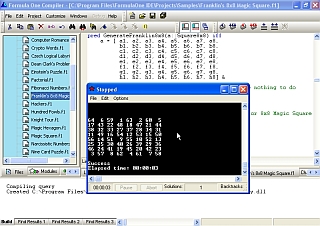
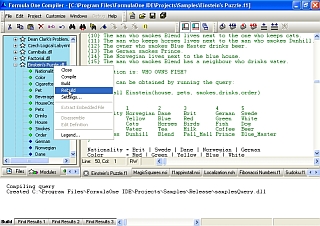
What Is FormulaOne?
FormulaOne is a constraint
logic programming (CLP) system for the development of applications. The design
preserves and incorporates the best features of the previous generations of
logical programming languages. FormulaOne is a compiler with an integrated
development environment, including a built-in editor and linker. FormulaOne's
compact grammar and powerful set of mechanisms for pattern matching,
backtracking and advanced data structures give it surprisingly powerful
techniques for handling problems involving symbolic computations. FormulaOne's
syntax leads to programs that are clear, concise and well structured. The power
of symbolic computation allows the FormulaOne programmer to work at a higher
level of abstraction, being concerned more with the nature of the program's
function and less with the "nuts and bolts" of how it will be
accomplished.
Until now the leading representative of 5th generation
languages was Prolog. Prolog, by means of built-in backtracking, introduced the
automatic processing of alternatives. For this to work every candidate solution
is generated and subjected to tests to see if it satisfies the given terms or
not. As an example, a problem of medium complexity might involve, say, 200
million backtracks and take 80 minutes to execute. FormulaOne, on the other
hand, will lop off the unneeded branches of the big decision tree and solve the
same problem in a few seconds with only a few hundreds of backtracks. This speed
and efficiency is achieved due to the implementation of a logic constraint
mechanism within its logic engine. FormulaOne is also a natural relational
database language. It can readily query one or more of its databases attaching
arbitrary retrieval conditions on a record or its fields using its symbolic
processing capability. FormulaOne employs sophisticated data types in defining
records and fields. A database record and/or field can be virtually of any type,
ranging from basic types such as integer, real number to types of variable
length such as strings, multiple precision integers, arrays, lists, enumerated
and even recursive types.
FormulaOne Features
- Windows 2000, XP, Vista, Windows 7 platforms.
- Integrated Environment - contains programmable editor, compiler, linker, query/run facility.
- Integrated NSIS (Nullsoft Scriptable Install System) compiler - easily create installable redistributable applications.
- Incremental Modular Compiler.
- Linker - linking FormulaOne modules into dynamically linked library modules (dll).
- Incremental Garbage Collection - facilitates optimal memory management.
- Automatic Cross-modular Type Checking - improves efficiency of routine testing.
- Types Supported - integer, multiple precision integer ("bignum"), real number, string, array, list, enumerated types, union (may be recursively defined, i.e. tree), structure of any type combination.
- Tail Recursion Optimization - enhances efficiency of recursions.
- Files Supported - Ascii, binary, indexed FormulaOne's database files with records of variable length of any type, variable length indices.